Difference between revisions of "AI understanding"
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Semanticity) |
KevinYager (talk | contribs) (→Psychology) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
** [https://transformer-circuits.pub/2025/attribution-graphs/methods.html Circuit Tracing: Revealing Computational Graphs in Language Models] | ** [https://transformer-circuits.pub/2025/attribution-graphs/methods.html Circuit Tracing: Revealing Computational Graphs in Language Models] | ||
** [https://transformer-circuits.pub/2025/attribution-graphs/biology.html On the Biology of a Large Language Model] | ** [https://transformer-circuits.pub/2025/attribution-graphs/biology.html On the Biology of a Large Language Model] | ||
| + | * 2025-11: OpenAI: [https://cdn.openai.com/pdf/41df8f28-d4ef-43e9-aed2-823f9393e470/circuit-sparsity-paper.pdf Weight-sparse transformers have interpretable circuits] ([https://openai.com/index/understanding-neural-networks-through-sparse-circuits/ blog]) | ||
| + | * 2026-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.13548 Patterning: The Dual of Interpretability] | ||
==Semanticity== | ==Semanticity== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 57: | ||
==Meta-cognition== | ==Meta-cognition== | ||
* 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13763 Language Models Are Capable of Metacognitive Monitoring and Control of Their Internal Activations] | * 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13763 Language Models Are Capable of Metacognitive Monitoring and Control of Their Internal Activations] | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.15674 Activation Oracles: Training and Evaluating LLMs as General-Purpose Activation Explainers] | ||
==Coding Models== | ==Coding Models== | ||
| Line 86: | Line 89: | ||
* 2025-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.08009 The Geometry of Prompting: Unveiling Distinct Mechanisms of Task Adaptation in Language Models] | * 2025-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.08009 The Geometry of Prompting: Unveiling Distinct Mechanisms of Task Adaptation in Language Models] | ||
* 2025-08: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10003 Semantic Structure in Large Language Model Embeddings] | * 2025-08: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2508.10003 Semantic Structure in Large Language Model Embeddings] | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.09782 The Geometry of Reasoning: Flowing Logics in Representation Space] | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://transformer-circuits.pub/2025/linebreaks/index.html When Models Manipulate Manifolds: The Geometry of a Counting Task] | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.26745 Deep sequence models tend to memorize geometrically; it is unclear why] | ||
==Topography== | ==Topography== | ||
| Line 101: | Line 107: | ||
* 2023-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.15936 A Theory for Emergence of Complex Skills in Language Models] | * 2023-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.15936 A Theory for Emergence of Complex Skills in Language Models] | ||
* 2024-06: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.19370v1 Emergence of Hidden Capabilities: Exploring Learning Dynamics in Concept Space] | * 2024-06: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.19370v1 Emergence of Hidden Capabilities: Exploring Learning Dynamics in Concept Space] | ||
| + | * 2025-06: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.01622 General agents contain world models] | ||
| + | * 2025-09: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.20328 Video models are zero-shot learners and reasoners] | ||
===Semantic Directions=== | ===Semantic Directions=== | ||
| Line 141: | Line 149: | ||
* [https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.13787 Looking Inward: Language Models Can Learn About Themselves by Introspection] | * [https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.13787 Looking Inward: Language Models Can Learn About Themselves by Introspection] | ||
* [https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11120 Tell me about yourself: LLMs are aware of their learned behaviors] | * [https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11120 Tell me about yourself: LLMs are aware of their learned behaviors] | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.22887 Infusing Theory of Mind into Socially Intelligent LLM Agents] | ||
===Skeptical=== | ===Skeptical=== | ||
| Line 172: | Line 181: | ||
* 2024-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.18624 How to explain grokking] | * 2024-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.18624 How to explain grokking] | ||
* 2024-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.09810 The Complexity Dynamics of Grokking] | * 2024-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.09810 The Complexity Dynamics of Grokking] | ||
| + | * 2025-09: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.21519 Provable Scaling Laws of Feature Emergence from Learning Dynamics of Grokking] | ||
===Tests of Resilience to Dropouts/etc.=== | ===Tests of Resilience to Dropouts/etc.=== | ||
| Line 215: | Line 225: | ||
* 2025-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.07951 Scaling Laws for Native Multimodal Models Scaling Laws for Native Multimodal Models] | * 2025-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.07951 Scaling Laws for Native Multimodal Models Scaling Laws for Native Multimodal Models] | ||
* 2025-05: [https://brendel-group.github.io/llm-line/ LLMs on the Line: Data Determines Loss-To-Loss Scaling Laws] | * 2025-05: [https://brendel-group.github.io/llm-line/ LLMs on the Line: Data Determines Loss-To-Loss Scaling Laws] | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.13786 The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs] | ||
=Information Processing/Storage= | =Information Processing/Storage= | ||
| Line 220: | Line 231: | ||
* 2021-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.00008 Why is AI hard and Physics simple?] | * 2021-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.00008 Why is AI hard and Physics simple?] | ||
* 2021-06: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.06981 Thinking Like Transformers] | * 2021-06: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.06981 Thinking Like Transformers] | ||
| + | * 2023-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.00948 Large Linguistic Models: Investigating LLMs' metalinguistic abilities] | ||
* "A transformer's depth affects its reasoning capabilities, whilst model size affects its knowledge capacity" ([https://x.com/danielhanchen/status/1835684061475655967 c.f.]) | * "A transformer's depth affects its reasoning capabilities, whilst model size affects its knowledge capacity" ([https://x.com/danielhanchen/status/1835684061475655967 c.f.]) | ||
** 2024-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.14905 MobileLLM: Optimizing Sub-billion Parameter Language Models for On-Device Use Cases] | ** 2024-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.14905 MobileLLM: Optimizing Sub-billion Parameter Language Models for On-Device Use Cases] | ||
| Line 228: | Line 240: | ||
* 2024-11: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.16679 Do Large Language Models Perform Latent Multi-Hop Reasoning without Exploiting Shortcuts?] | * 2024-11: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.16679 Do Large Language Models Perform Latent Multi-Hop Reasoning without Exploiting Shortcuts?] | ||
* 2025-03: [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2503.03961 A Little Depth Goes a Long Way: The Expressive Power of Log-Depth Transformers] | * 2025-03: [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2503.03961 A Little Depth Goes a Long Way: The Expressive Power of Log-Depth Transformers] | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22471 The Bayesian Geometry of Transformer Attention] | ||
| + | * 2026-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03220 From Entropy to Epiplexity: Rethinking Information for Computationally Bounded Intelligence] | ||
==Statistics/Math== | ==Statistics/Math== | ||
| Line 284: | Line 298: | ||
* 2015-11: [https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07543 Convergent Learning: Do different neural networks learn the same representations?] | * 2015-11: [https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.07543 Convergent Learning: Do different neural networks learn the same representations?] | ||
* 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.12540 Harnessing the Universal Geometry of Embeddings]: Evidence for [https://x.com/jxmnop/status/1925224620166128039 The Strong Platonic Representation Hypothesis]; models converge to a single consensus reality | * 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.12540 Harnessing the Universal Geometry of Embeddings]: Evidence for [https://x.com/jxmnop/status/1925224620166128039 The Strong Platonic Representation Hypothesis]; models converge to a single consensus reality | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.03750 Universally Converging Representations of Matter Across Scientific Foundation Models] | ||
==Function Approximation== | ==Function Approximation== | ||
| Line 295: | Line 310: | ||
* 2025-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.20545 SoS1: O1 and R1-Like Reasoning LLMs are Sum-of-Square Solvers] | * 2025-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.20545 SoS1: O1 and R1-Like Reasoning LLMs are Sum-of-Square Solvers] | ||
* 2025-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.21212 Transformers Learn to Implement Multi-step Gradient Descent with Chain of Thought] | * 2025-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.21212 Transformers Learn to Implement Multi-step Gradient Descent with Chain of Thought] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Physics Based= | ||
| + | * 2014-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/1401.1219 Consciousness as a State of Matter] | ||
| + | * 2016-08: [https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08225 Why does deep and cheap learning work so well?] | ||
| + | * 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.23489 SGD as Free Energy Minimization: A Thermodynamic View on Neural Network Training] | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2523012122 Heavy-tailed update distributions arise from information-driven self-organization in nonequilibrium learning] | ||
=Failure Modes= | =Failure Modes= | ||
| Line 309: | Line 330: | ||
* 2024-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.03211 How Does Quantization Affect Multilingual LLMs?]: Quantization degrades different languages by differing amounts | * 2024-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.03211 How Does Quantization Affect Multilingual LLMs?]: Quantization degrades different languages by differing amounts | ||
* 2025-03: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.10061v1 Compute Optimal Scaling of Skills: Knowledge vs Reasoning]: Scaling laws are skill-dependent | * 2025-03: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.10061v1 Compute Optimal Scaling of Skills: Knowledge vs Reasoning]: Scaling laws are skill-dependent | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.18212 A Definition of AGI] | ||
===See also=== | ===See also=== | ||
* [[AI_understanding|AI Understanding]] > [[AI_understanding#Psychology|Psychology]] > [[AI_understanding#LLM_personalities|LLM personalities]] | * [[AI_understanding|AI Understanding]] > [[AI_understanding#Psychology|Psychology]] > [[AI_understanding#LLM_personalities|LLM personalities]] | ||
* [[AI tricks]] > [[AI_tricks#Prompt_Engineering|Prompt Engineering]] > [[AI_tricks#Brittleness|Brittleness]] | * [[AI tricks]] > [[AI_tricks#Prompt_Engineering|Prompt Engineering]] > [[AI_tricks#Brittleness|Brittleness]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Conversely (AI models converge)=== | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2512.03750 Universally Converging Representations of Matter Across Scientific Foundation Models] | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.05117 The Universal Weight Subspace Hypothesis] | ||
| + | * 2026-01: [https://avikrishna.substack.com/p/eliciting-frontier-model-character Eliciting Frontier Model Character Training: A study of personality convergence across language models] | ||
==Model Collapse== | ==Model Collapse== | ||
| Line 321: | Line 348: | ||
* 2024-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.03502 AI and the Problem of Knowledge Collapse] | * 2024-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.03502 AI and the Problem of Knowledge Collapse] | ||
* 2024-07: [https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07566-y AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data] | * 2024-07: [https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07566-y AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data] | ||
| + | * 2026-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.05280 On the Limits of Self-Improving in LLMs and Why AGI, ASI and the Singularity Are Not Near Without Symbolic Model Synthesis] | ||
===Analysis=== | ===Analysis=== | ||
| Line 339: | Line 367: | ||
* 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.17117 From Tokens to Thoughts: How LLMs and Humans Trade Compression for Meaning] | * 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.17117 From Tokens to Thoughts: How LLMs and Humans Trade Compression for Meaning] | ||
* 2025-07: [https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5357179 Call Me A Jerk: Persuading AI to Comply with Objectionable Requests] | * 2025-07: [https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5357179 Call Me A Jerk: Persuading AI to Comply with Objectionable Requests] | ||
| + | * 2026-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.06047 "They parted illusions -- they parted disclaim marinade": Misalignment as structural fidelity in LLMs] | ||
| + | * 2026-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.02606 Gender Dynamics and Homophily in a Social Network of LLM Agents] | ||
| + | * 2026-02: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2602.01689 What LLMs Think When You Don't Tell Them What to Think About?] | ||
==Allow LLM to think== | ==Allow LLM to think== | ||
| Line 369: | Line 400: | ||
* 2025-08: [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2508.01191 Is Chain-of-Thought Reasoning of LLMs a Mirage? A Data Distribution Lens] | * 2025-08: [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2508.01191 Is Chain-of-Thought Reasoning of LLMs a Mirage? A Data Distribution Lens] | ||
| − | ==Self-Awareness and Self-Recognition== | + | ==Self-Awareness and Self-Recognition and Introspection== |
| + | * 2022-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.05221 Language Models (Mostly) Know What They Know] | ||
| + | * 2024-04: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.13076 LLM Evaluators Recognize and Favor Their Own Generations] | ||
* 2024-09: [https://situational-awareness-dataset.org/ Me, Myself and AI: The Situational Awareness Dataset for LLMs] | * 2024-09: [https://situational-awareness-dataset.org/ Me, Myself and AI: The Situational Awareness Dataset for LLMs] | ||
| + | * 2024-10: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.13787 Looking Inward: Language Models Can Learn About Themselves by Introspection] | ||
* 2024-12: [https://theaidigest.org/self-awareness AIs are becoming more self-aware. Here's why that matters] | * 2024-12: [https://theaidigest.org/self-awareness AIs are becoming more self-aware. Here's why that matters] | ||
| + | * 2025-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.11120 Tell me about yourself: LLMs are aware of their learned behaviors] | ||
* 2025-04: [https://x.com/Josikinz/status/1907923319866716629 LLMs can guess which comic strip was generated by themselves (vs. other LLM)] | * 2025-04: [https://x.com/Josikinz/status/1907923319866716629 LLMs can guess which comic strip was generated by themselves (vs. other LLM)] | ||
* 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13763 Language Models Are Capable of Metacognitive Monitoring and Control of Their Internal Activations] | * 2025-05: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.13763 Language Models Are Capable of Metacognitive Monitoring and Control of Their Internal Activations] | ||
| + | * 2025-10: [https://transformer-circuits.pub/2025/introspection/index.html Emergent Introspective Awareness in Large Language Models] (Anthropic, [https://www.anthropic.com/research/introspection blog]) | ||
| + | * 2025-12: [https://www.arxiv.org/abs/2512.24661 Do Large Language Models Know What They Are Capable Of?] | ||
==LLM personalities== | ==LLM personalities== | ||
* 2025-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.02618 Strategic Intelligence in Large Language Models: Evidence from evolutionary Game Theory] | * 2025-07: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.02618 Strategic Intelligence in Large Language Models: Evidence from evolutionary Game Theory] | ||
* 2025-09: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.04343 Psychologically Enhanced AI Agents] | * 2025-09: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.04343 Psychologically Enhanced AI Agents] | ||
| + | * 2026-01: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.10387 The Assistant Axis: Situating and Stabilizing the Default Persona of Language Models] | ||
==Quirks & Biases== | ==Quirks & Biases== | ||
* 2025-04: [https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/judgment-and-decision-making/article/artificial-intelligence-and-dichotomania/0421D2310727D73FAB47069FD1620AA1 Artificial intelligence and dichotomania] | * 2025-04: [https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/judgment-and-decision-making/article/artificial-intelligence-and-dichotomania/0421D2310727D73FAB47069FD1620AA1 Artificial intelligence and dichotomania] | ||
| + | * 2025-09: [https://arxiv.org/abs/2509.22818 Can Large Language Models Develop Gambling Addiction?] | ||
=Vision Models= | =Vision Models= | ||
| Line 388: | Line 427: | ||
=See Also= | =See Also= | ||
| + | * [[AI]] | ||
* [[AI tools]] | * [[AI tools]] | ||
* [[AI agents]] | * [[AI agents]] | ||
* [[Robots]] | * [[Robots]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:30, 9 February 2026
Contents
Interpretability
- 2017-01: Learning to Generate Reviews and Discovering Sentiment
- 2025-02: Neural Interpretable Reasoning
Concepts
- 2025-04: Towards Understanding the Nature of Attention with Low-Rank Sparse Decomposition (code)
- 2025-08: Tracing Attention Computation Through Feature Interactions
Mechanistic Interpretability
- 2020-03: OpenAI: Zoom In: An Introduction to Circuits
- 2021-12: Anthropic: A Mathematical Framework for Transformer Circuits
- 2022-09: Interpretability in the Wild: a Circuit for Indirect Object Identification in GPT-2 Small
- 2023-01: Tracr: Compiled Transformers as a Laboratory for Interpretability (code)
- 2024-07: Anthropic: Circuits Update
- 2025-01: Interpretability in Parameter Space: Minimizing Mechanistic Description Length with Attribution-based Parameter Decomposition (blog post)
- 2025-01: Review: Open Problems in Mechanistic Interpretability
- 2025-03: Anthropic: Tracing the thoughts of a large language model
- 2025-11: OpenAI: Weight-sparse transformers have interpretable circuits (blog)
- 2026-01: Patterning: The Dual of Interpretability
Semanticity
- 2023-09: Sparse Autoencoders Find Highly Interpretable Features in Language Models
- Anthropic monosemanticity interpretation of LLM features:
- 2024-06: OpenaAI: Scaling and evaluating sparse autoencoders
- 2024-08: Showing SAE Latents Are Not Atomic Using Meta-SAEs (demo)
- 2024-10: Efficient Dictionary Learning with Switch Sparse Autoencoders (code) More efficient SAE generation
- 2024-10: Decomposing The Dark Matter of Sparse Autoencoders (code) Shows that SAE errors are predictable
- 2024-10: Automatically Interpreting Millions of Features in Large Language Models
- 2024-10: Beyond Interpretability: The Gains of Feature Monosemanticity on Model Robustness
- 2024-12: Monet: Mixture of Monosemantic Experts for Transformers
- 2024-12: Matryoshka Sparse Autoencoders
- 2024-12: Learning Multi-Level Features with Matryoshka SAEs
- 2025-01: Low-Rank Adapting Models for Sparse Autoencoders
- 2025-02: Universal Sparse Autoencoders: Interpretable Cross-Model Concept Alignment
- 2025-02: Sparse Autoencoders for Scientifically Rigorous Interpretation of Vision Models
- 2025-03: Steering Large Language Model Activations in Sparse Spaces
- 2025-03: Beyond Matryoshka: Revisiting Sparse Coding for Adaptive Representation
- 2025-03: From superposition to sparse codes: interpretable representations in neural networks
- 2025-03: I Have Covered All the Bases Here: Interpreting Reasoning Features in Large Language Models via Sparse Autoencoders
- 2025-05: SAEs Are Good for Steering -- If You Select the Right Features
- 2025-06: Dense SAE Latents Are Features, Not Bugs
- 2025-06: Stochastic Parameter Decomposition (code, blog)
- 2025-08: Semantic Structure in Large Language Model Embeddings
Counter-Results
- 2020-10: Towards falsifiable interpretability research
- 2025-01: Sparse Autoencoders Trained on the Same Data Learn Different Features
- 2025-01: AxBench: Steering LLMs? Even Simple Baselines Outperform Sparse Autoencoders
- 2025-01: Sparse Autoencoders Can Interpret Randomly Initialized Transformers
- 2025-02: Sparse Autoencoders Do Not Find Canonical Units of Analysis
- 2025-03: Negative Results for SAEs On Downstream Tasks and Deprioritising SAE Research
Meta-cognition
- 2025-05: Language Models Are Capable of Metacognitive Monitoring and Control of Their Internal Activations
- 2025-12: Activation Oracles: Training and Evaluating LLMs as General-Purpose Activation Explainers
Coding Models
- Sparse Auto Encoders: See Semanticity.
- dictionary_learning
- Predicting Future Activations
- 2024-06: Transcoders Find Interpretable LLM Feature Circuits
- 2024-10: Sparse Crosscoders for Cross-Layer Features and Model Diffing
Reward Functions
Symbolic and Notation
- A Mathematical Framework for Transformer Circuits
- Beyond Euclid: An Illustrated Guide to Modern Machine Learning with Geometric, Topological, and Algebraic Structures
- 2024-07: On the Anatomy of Attention: Introduces category-theoretic diagrammatic formalism for DL architectures
- 2024-11: diagrams to represent algorithms
- 2024-12: FlashAttention on a Napkin: A Diagrammatic Approach to Deep Learning IO-Awareness
Mathematical
Geometric
- 2023-11: The Linear Representation Hypothesis and the Geometry of Large Language Models
- 2024-06: The Geometry of Categorical and Hierarchical Concepts in Large Language Models
- Natural hierarchies of concepts---which occur throughout natural language and especially in scientific ontologies---are represented in the model's internal vectorial space as polytopes that can be decomposed into simplexes of mutually-exclusive categories.
- 2024-07: Reasoning in Large Language Models: A Geometric Perspective
- 2024-09: Deep Manifold Part 1: Anatomy of Neural Network Manifold
- 2024-10: The Geometry of Concepts: Sparse Autoencoder Feature Structure
- Tegmark et al. report multi-scale structure: 1) “atomic” small-scale, 2) “brain” intermediate-scale, and 3) “galaxy” large-scale
- 2025-02: The Geometry of Prompting: Unveiling Distinct Mechanisms of Task Adaptation in Language Models
- 2025-08: Semantic Structure in Large Language Model Embeddings
- 2025-10: The Geometry of Reasoning: Flowing Logics in Representation Space
- 2025-10: When Models Manipulate Manifolds: The Geometry of a Counting Task
- 2025-10: Deep sequence models tend to memorize geometrically; it is unclear why
Topography
Challenges
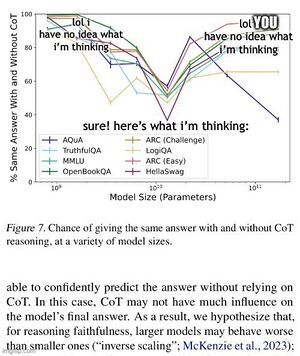
- 2023-07Jul: Measuring Faithfulness in Chain-of-Thought Reasoning roughly proves that sufficiently large models do not generate CoT that actually captures their internal reasoning)
Heuristic Understanding
- 2022-09: Janus: Simulators
Emergent Internal Model Building
- 2023-07: A Theory for Emergence of Complex Skills in Language Models
- 2024-06: Emergence of Hidden Capabilities: Exploring Learning Dynamics in Concept Space
- 2025-06: General agents contain world models
- 2025-09: Video models are zero-shot learners and reasoners
Semantic Directions
Directions, e.g.: f(king)-f(man)+f(woman)=f(queen) or f(sushi)-f(Japan)+f(Italy)=f(pizza)
- Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space
- Linguistic Regularities in Continuous Space Word Representations
- Word Embeddings, Analogies, and Machine Learning: Beyond king - man + woman = queen
- Glove: Global vectors for word representation
- Using Word2Vec to process big text data
- The geometry of truth: Emergent linear structure in large language model representations of true/false datasets (true/false)
- Monotonic Representation of Numeric Properties in Language Models (numeric directions)
Task vectors:
- Function Vectors in Large Language Models
- In-context learning creates task vectors
- Extracting sae task features for in-context learning
- Emergence of Abstractions: Concept Encoding and Decoding Mechanism for In-Context Learning in Transformers
Reasoning:
Feature Geometry Reproduces Problem-space
- Emergent World Representations: Exploring a Sequence Model Trained on a Synthetic Task (Othello)
- Emergent linear representations in world models of self-supervised sequence models (Othello)
- What learning algorithm is in-context learning? Investigations with linear models
- Emergent analogical reasoning in large language models
- Language Models Represent Space and Time (Maps of world, US)
- Not All Language Model Features Are Linear (Days of week form ring, etc.)
- Evaluating the World Model Implicit in a Generative Model (Map of Manhattan)
- Reliable precipitation nowcasting using probabilistic diffusion models. Generation of precipitation map imagery is predictive of actual future weather; implies model is learning scientifically-relevant modeling.
- The Platonic Representation Hypothesis: Different models (including across modalities) are converging to a consistent world model.
- ICLR: In-Context Learning of Representations
- Language Models Use Trigonometry to Do Addition: Numbers arranged in helix to enable addition
Capturing Physics
- 2020-09: Learning to Identify Physical Parameters from Video Using Differentiable Physics
- 2022-07: Self-Supervised Learning for Videos: A Survey
- 2025-02: Fair at Meta: Intuitive physics understanding emerges from self-supervised pretraining on natural videos
Theory of Mind
- Evaluating Large Language Models in Theory of Mind Tasks
- Looking Inward: Language Models Can Learn About Themselves by Introspection
- Tell me about yourself: LLMs are aware of their learned behaviors
- 2025-10: Infusing Theory of Mind into Socially Intelligent LLM Agents
Skeptical
- 2025-01: Do generative video models learn physical principles from watching videos? (project, code)
- 2025-06: The Illusion of Thinking: Understanding the Strengths and Limitations of Reasoning Models via the Lens of Problem Complexity
- 2025-06: Potemkin Understanding in Large Language Models
- 2025-06: Do Vision-Language Models Have Internal World Models? Towards an Atomic Evaluation
Information Processing
- 2019-03: Diagnosing and Enhancing VAE Models
- 2021-03: Pretrained Transformers as Universal Computation Engines
- 2022-10: How Mask Matters: Towards Theoretical Understandings of Masked Autoencoders
- 2023-04: Why think step by step? Reasoning emerges from the locality of experience
- 2023-10: What's the Magic Word? A Control Theory of LLM Prompting
- 2024-02: Chain of Thought Empowers Transformers to Solve Inherently Serial Problems: Proves that transformers can solve any problem, if they can generate sufficient intermediate tokens
- 2024-07: Physics of Language Models: Part 2.1, Grade-School Math and the Hidden Reasoning Process
- Models learning reasoning skills (they are not merely memorizing solution templates). They can mentally generate simple short plans (like humans).
- When presented facts, models develop internal understanding of what parameters (recursively) depend on each other. This occurs even before an explicit question is asked (i.e. before the task is defined). This appears to be different from human reasoning.
- Model depth matters for reasoning. This cannot be mitigated by chain-of-thought prompting (which allow models to develop and then execute plans) since even a single CoT step may require deep, multi-step reasoning/planning.
- 2024-11: Ask, and it shall be given: Turing completeness of prompting
- 2025-04: Layers at Similar Depths Generate Similar Activations Across LLM Architectures
Generalization
- 2024-06: Connecting the Dots: LLMs can Infer and Verbalize Latent Structure from Disparate Training Data
Grokking
- 2022-01: Grokking: Generalization Beyond Overfitting on Small Algorithmic Datasets
- 2022-05: Towards Understanding Grokking: An Effective Theory of Representation Learning
- 2024-01: Critical Data Size of Language Models from a Grokking Perspective
- 2024-02: Unified View of Grokking, Double Descent and Emergent Abilities: A Perspective from Circuits Competition
- 2024-12: How to explain grokking
- 2024-12: The Complexity Dynamics of Grokking
- 2025-09: Provable Scaling Laws of Feature Emergence from Learning Dynamics of Grokking
Tests of Resilience to Dropouts/etc.
- 2024-02: Explorations of Self-Repair in Language Models
- 2024-06: What Matters in Transformers? Not All Attention is Needed
- Removing entire transformer blocks leads to significant performance degradation
- Removing MLP layers results in significant performance degradation
- Removing attention layers causes almost no performance degradation
- E.g. half of attention layers are deleted (48% speed-up), leads to only 2.4% decrease in the benchmarks
- 2024-06: The Remarkable Robustness of LLMs: Stages of Inference?
- They intentionally break the network (swapping layers), yet it continues to work remarkably well. This suggests LLMs are quite robust, and allows them to identify different stages in processing.
- They also use these interventions to infer what different layers are doing. They break apart the LLM transformer layers into four stages:
- Detokenization: Raw tokens are converted into meaningful entities that take into account local context (especially using nearby tokens).
- Feature engineering: Features are progressively refined. Factual knowledge is leveraged.
- Prediction ensembling: Predictions (for the ultimately-selected next-token) emerge. A sort of consensus voting is used, with “prediction neurons” and "suppression neurons" playing a major role in upvoting/downvoting.
- Residual sharpening: The semantic representations are collapsed into specific next-token predictions. There is a strong emphasis on suppression neurons eliminating options. The confidence is calibrated.
- This structure can be thought of as two halves (being roughly dual to each other): the first half broadens (goes from distinct tokens to a rich/elaborate concept-space) and the second half collapses (goes from rich concepts to concrete token predictions).
Semantic Vectors
- 2024-06: Refusal in Language Models Is Mediated by a Single Direction
- 2025-02: Emergent Misalignment: Narrow finetuning can produce broadly misaligned LLMs (demonstrates entangling of concepts into a single preference vector)
- 2025-03: Analogical Reasoning Inside Large Language Models: Concept Vectors and the Limits of Abstraction
Other
- 2024-11: Deep Learning Through A Telescoping Lens: A Simple Model Provides Empirical Insights On Grokking, Gradient Boosting & Beyond
- 2024-11: Language Models are Hidden Reasoners: Unlocking Latent Reasoning Capabilities via Self-Rewarding (code)
- 2024-11: Procedural Knowledge in Pretraining Drives Reasoning in Large Language Models: LLMs learn reasoning by extracting procedures from training data, not by memorizing specific answers
- 2024-11: LLMs Do Not Think Step-by-step In Implicit Reasoning
- 2024-12: The Complexity Dynamics of Grokking
Scaling Laws
- 1993: Learning Curves: Asymptotic Values and Rate of Convergence
- 2017-12: Deep Learning Scaling is Predictable, Empirically (Baidu)
- 2019-03: The Bitter Lesson (Rich Sutton)
- 2020-01: Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models (OpenAI)
- 2020-10: Scaling Laws for Autoregressive Generative Modeling (OpenAI)
- 2020-05: The Scaling Hypothesis (Gwern)
- 2021-08: Scaling Laws for Deep Learning
- 2021-02: Explaining Neural Scaling Laws (Google DeepMind)
- 2022-03: Training Compute-Optimal Large Language Models (Chinchilla, Google DeepMind)
- 2025-03: Predictable Scale: Part I -- Optimal Hyperparameter Scaling Law in Large Language Model Pretraining
- 2025-03: Compute Optimal Scaling of Skills: Knowledge vs Reasoning
- 2025-04: Scaling Laws for Native Multimodal Models Scaling Laws for Native Multimodal Models
- 2025-05: LLMs on the Line: Data Determines Loss-To-Loss Scaling Laws
- 2025-10: The Art of Scaling Reinforcement Learning Compute for LLMs
Information Processing/Storage
- 2020-02: A Theory of Usable Information Under Computational Constraints
- 2021-04: Why is AI hard and Physics simple?
- 2021-06: Thinking Like Transformers
- 2023-05: Large Linguistic Models: Investigating LLMs' metalinguistic abilities
- "A transformer's depth affects its reasoning capabilities, whilst model size affects its knowledge capacity" (c.f.)
- 2024-02: MobileLLM: Optimizing Sub-billion Parameter Language Models for On-Device Use Cases
- 2024-04: The Illusion of State in State-Space Models (figure 3)
- 2024-08: Gemma 2: Improving Open Language Models at a Practical Size (table 9)
- 2024-09: Schrodinger's Memory: Large Language Models
- 2024-10: Deciphering the Factors Influencing the Efficacy of Chain-of-Thought: Probability, Memorization, and Noisy Reasoning. CoT involves both memorization and (probabilitic) reasoning
- 2024-11: Do Large Language Models Perform Latent Multi-Hop Reasoning without Exploiting Shortcuts?
- 2025-03: A Little Depth Goes a Long Way: The Expressive Power of Log-Depth Transformers
- 2025-12: The Bayesian Geometry of Transformer Attention
- 2026-01: From Entropy to Epiplexity: Rethinking Information for Computationally Bounded Intelligence
Statistics/Math
- 2023-05: The emergence of clusters in self-attention dynamics
- 2023-12: A mathematical perspective on Transformers
- 2024-07: Understanding Transformers via N-gram Statistics
- 2024-10: Dynamic metastability in the self-attention model
- 2024-11: Measure-to-measure interpolation using Transformers
- 2025-04: Quantitative Clustering in Mean-Field Transformer Models
Tokenization
For numbers/math
- 2024-02: Tokenization counts: the impact of tokenization on arithmetic in frontier LLMs: L2R vs. R2L yields different performance on math
Data Storage
- 1988-09: On the capabilities of multilayer perceptrons
- 2006-12: Geometrical and Statistical Properties of Systems of Linear Inequalities with Applications in Pattern Recognition (single-layer perceptron stores >2 bits/parameter; MLP ~ 2*N2 bits w/ N2 params)
- 2016-11: Capacity and Trainability in Recurrent Neural Networks (5 bits/param)
- 2018-02: The Secret Sharer: Evaluating and Testing Unintended Memorization in Neural Networks
- 2019-05: Memorization Capacity of Deep Neural Networks under Parameter Quantization
- 2020-02: How Much Knowledge Can You Pack Into the Parameters of a Language Model?
- 2020-08: Language Models as Knowledge Bases: On Entity Representations, Storage Capacity, and Paraphrased Queries (capacity scales linearly with parameters; more training samples leads to less memorization)
- 2020-12: When is Memorization of Irrelevant Training Data Necessary for High-Accuracy Learning?
- 2024-04: Physics of Language Models: Part 3.3, Knowledge Capacity Scaling Laws (2 bits/param)
- 2024-06: Scaling Laws for Fact Memorization of Large Language Models (1T params needed to memorize Wikipedia)
- 2024-12: The Complexity Dynamics of Grokking
- 2025-05: How much do language models memorize? (3.6 bits/parameter)
- 2025-06: Trade-offs in Data Memorization via Strong Data Processing Inequalities
Reverse-Engineering Training Data
- 2025-06: Can We Infer Confidential Properties of Training Data from LLMs?
- 2025-06: Approximating Language Model Training Data from Weights
Compression
- 2022-12: Less is More: Parameter-Free Text Classification with Gzip
- 2023-06: LLMZip: Lossless Text Compression using Large Language Models
- 2023-07: “Low-Resource” Text Classification: A Parameter-Free Classification Method with Compressors
- 2023-09: Language Modeling Is Compression
- 2024-06: An Image is Worth 32 Tokens for Reconstruction and Generation
Learning/Training
- 2018-03: The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis: Finding Sparse, Trainable Neural Networks: Sparse neural networks are optimal, but it is difficult to identify the right architecture and train it. Deep learning typically consists of training a dense neural network, which makes it easier to learn an internal sparse circuit optimal to a particular problem.
- 2024-12: On the Ability of Deep Networks to Learn Symmetries from Data: A Neural Kernel Theory
- 2025-01: Physics of Skill Learning
- 2025-05: ProRL: Prolonged Reinforcement Learning Expands Reasoning Boundaries in Large Language Models
Cross-modal knowledge transfer
- 2022-03: Leveraging Visual Knowledge in Language Tasks: An Empirical Study on Intermediate Pre-training for Cross-modal Knowledge Transfer
- 2023-05: Towards Versatile and Efficient Visual Knowledge Integration into Pre-trained Language Models with Cross-Modal Adapters
- 2025-02: Sparse Autoencoders for Scientifically Rigorous Interpretation of Vision Models: CLIP learns richer set of aggregated representations (e.g. for a culture or country), vs. a vision-only model.
Hidden State
- 2025-02: Emergent Response Planning in LLM: They show that the latent representation contains information beyond that needed for the next token (i.e. the model learns to "plan ahead" and encode information relevant to future tokens)
- 2025-03: (How) Do Language Models Track State?
Convergent Representation
- 2015-11: Convergent Learning: Do different neural networks learn the same representations?
- 2025-05: Harnessing the Universal Geometry of Embeddings: Evidence for The Strong Platonic Representation Hypothesis; models converge to a single consensus reality
- 2025-12: Universally Converging Representations of Matter Across Scientific Foundation Models
Function Approximation
- 2022-08: What Can Transformers Learn In-Context? A Case Study of Simple Function Classes: can learn linear functions (equivalent to least-squares estimator)
- 2022-11: Teaching Algorithmic Reasoning via In-context Learning: Simple arithmetic
- 2022-11: What learning algorithm is in-context learning? Investigations with linear models (code): can learn linear regression
- 2022-12: Transformers learn in-context by gradient descent
- 2023-06: Transformers learn to implement preconditioned gradient descent for in-context learning
- 2023-07: One Step of Gradient Descent is Provably the Optimal In-Context Learner with One Layer of Linear Self-Attention
- 2024-04: ChatGLM-Math: Improving Math Problem-Solving in Large Language Models with a Self-Critique Pipeline
- 2025-02: SoS1: O1 and R1-Like Reasoning LLMs are Sum-of-Square Solvers
- 2025-02: Transformers Learn to Implement Multi-step Gradient Descent with Chain of Thought
Physics Based
- 2014-01: Consciousness as a State of Matter
- 2016-08: Why does deep and cheap learning work so well?
- 2025-05: SGD as Free Energy Minimization: A Thermodynamic View on Neural Network Training
- 2025-12: Heavy-tailed update distributions arise from information-driven self-organization in nonequilibrium learning
Failure Modes
- 2023-06: Can Large Language Models Infer Causation from Correlation?: Poor causal inference
- 2023-09: The Reversal Curse: LLMs trained on "A is B" fail to learn "B is A"
- 2023-09: Embers of Autoregression: Understanding Large Language Models Through the Problem They are Trained to Solve (biases towards "common" numbers, in-context CoT can reduce performance by incorrectly priming, etc.)
- 2023-11: Visual cognition in multimodal large language models (models lack human-like visual understanding)
Fracture Representation
- 2025-05: Questioning Representational Optimism in Deep Learning: The Fractured Entangled Representation Hypothesis (code)
Jagged Frontier
- 2023-09: Navigating the Jagged Technological Frontier: Field Experimental Evidence of the Effects of AI on Knowledge Worker Productivity and Quality
- 2024-07: How Does Quantization Affect Multilingual LLMs?: Quantization degrades different languages by differing amounts
- 2025-03: Compute Optimal Scaling of Skills: Knowledge vs Reasoning: Scaling laws are skill-dependent
- 2025-10: A Definition of AGI
See also
Conversely (AI models converge)
- 2025-12: Universally Converging Representations of Matter Across Scientific Foundation Models
- 2025-12: The Universal Weight Subspace Hypothesis
- 2026-01: Eliciting Frontier Model Character Training: A study of personality convergence across language models
Model Collapse
- 2023-05: The Curse of Recursion: Training on Generated Data Makes Models Forget
- 2023-07: Self-Consuming Generative Models Go MAD
- 2023-10: On the Stability of Iterative Retraining of Generative Models on their own Data
- 2023-11: Nepotistically Trained Generative-AI Models Collapse
- 2024-04: AI and the Problem of Knowledge Collapse
- 2024-07: AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data
- 2026-01: On the Limits of Self-Improving in LLMs and Why AGI, ASI and the Singularity Are Not Near Without Symbolic Model Synthesis
Analysis
- 2024-02: Scaling laws for learning with real and surrogate data
- 2024-12: Rate of Model Collapse in Recursive Training
Mitigation
- 2024-02: Model Collapse Demystified: The Case of Regression
- 2024-03: Common 7B Language Models Already Possess Strong Math Capabilities
- 2024-04: Is Model Collapse Inevitable? Breaking the Curse of Recursion by Accumulating Real and Synthetic Data
- 2024-06: Beyond Model Collapse: Scaling Up with Synthesized Data Requires Verification
- 2024-07: LLM See, LLM Do: Guiding Data Generation to Target Non-Differentiable Objectives
- 2024-08: Multilingual Arbitrage: Optimizing Data Pools to Accelerate Multilingual Progress
- 2025-03: Convergence Dynamics and Stabilization Strategies of Co-Evolving Generative Models
Psychology
- 2023-04: Inducing anxiety in large language models can induce bias
- 2025-05: From Tokens to Thoughts: How LLMs and Humans Trade Compression for Meaning
- 2025-07: Call Me A Jerk: Persuading AI to Comply with Objectionable Requests
- 2026-01: "They parted illusions -- they parted disclaim marinade": Misalignment as structural fidelity in LLMs
- 2026-02: Gender Dynamics and Homophily in a Social Network of LLM Agents
- 2026-02: What LLMs Think When You Don't Tell Them What to Think About?
Allow LLM to think
In-context Learning
- 2021-10: MetaICL: Learning to Learn In Context
- 2022-02: Rethinking the Role of Demonstrations: What Makes In-Context Learning Work?
- 2022-08: What Can Transformers Learn In-Context? A Case Study of Simple Function Classes
- 2022-11: What learning algorithm is in-context learning? Investigations with linear models
- 2022-12: Transformers learn in-context by gradient descent
- 2025-07: Learning without training: The implicit dynamics of in-context learning
Reasoning (CoT, etc.)
- 2025-01: Large Language Models Think Too Fast To Explore Effectively
- 2025-01: Thoughts Are All Over the Place: On the Underthinking of o1-Like LLMs
- 2025-01: Are DeepSeek R1 And Other Reasoning Models More Faithful?: reasoning models can provide faithful explanations for why their reasoning is correct
- 2025-03: Chain-of-Thought Reasoning In The Wild Is Not Always Faithful
- 2025-04: Rethinking Reflection in Pre-Training: pre-training alone already provides some amount of reflection/reasoning
- 2025-07: BRiTE: Bootstrapping Reinforced Thinking Process to Enhance Language Model Reasoning
Pathfinding
- 2024-08: DeepSeek-Prover-V1.5: Harnessing Proof Assistant Feedback for Reinforcement Learning and Monte-Carlo Tree Search
- 2025-06: Beyond the 80/20 Rule: High-Entropy Minority Tokens Drive Effective Reinforcement Learning for LLM Reasoning
- 2025-09: Tree-OPO: Off-policy Monte Carlo Tree-Guided Advantage Optimization for Multistep Reasoning
- 2025-09: Reverse-Engineered Reasoning for Open-Ended Generation
Skeptical
- 2025-06: The Illusion of Thinking: Understanding the Strengths and Limitations of Reasoning Models via the Lens of Problem Complexity
- 2025-08: Is Chain-of-Thought Reasoning of LLMs a Mirage? A Data Distribution Lens
Self-Awareness and Self-Recognition and Introspection
- 2022-07: Language Models (Mostly) Know What They Know
- 2024-04: LLM Evaluators Recognize and Favor Their Own Generations
- 2024-09: Me, Myself and AI: The Situational Awareness Dataset for LLMs
- 2024-10: Looking Inward: Language Models Can Learn About Themselves by Introspection
- 2024-12: AIs are becoming more self-aware. Here's why that matters
- 2025-01: Tell me about yourself: LLMs are aware of their learned behaviors
- 2025-04: LLMs can guess which comic strip was generated by themselves (vs. other LLM)
- 2025-05: Language Models Are Capable of Metacognitive Monitoring and Control of Their Internal Activations
- 2025-10: Emergent Introspective Awareness in Large Language Models (Anthropic, blog)
- 2025-12: Do Large Language Models Know What They Are Capable Of?
LLM personalities
- 2025-07: Strategic Intelligence in Large Language Models: Evidence from evolutionary Game Theory
- 2025-09: Psychologically Enhanced AI Agents
- 2026-01: The Assistant Axis: Situating and Stabilizing the Default Persona of Language Models
Quirks & Biases
- 2025-04: Artificial intelligence and dichotomania
- 2025-09: Can Large Language Models Develop Gambling Addiction?
Vision Models
- 2017-11: Distill: Feature Visualization: How neural networks build up their understanding of images
- 2021-01: Position, Padding and Predictions: A Deeper Look at Position Information in CNNs
- 2025-04: Perception Encoder: The best visual embeddings are not at the output of the network (code)